Содержание
Feature Overview
The ISDN Network Side for ETSI Net5 PRI feature enables Cisco IOS to replicate the public switched network interface to a PBX that is compatible with the ETSI Net5 switch type.
Routers and PBXs are both traditionally CPE with respect to the public switched network interfaces. For Voice over IP (VoIP) applications, it is desirable to interface access servers to PBXs with the access server representing the public switched network.
Enterprise organizations use the current VoIP features with Cisco products as a method to reduce long distance costs for phone calls within and outside of their organizations. However, there are times that a call cannot go over VoIP and the call needs to be placed using the PSTN. The customer then must have two devices connected to a PBX to allow some calls to be placed using VoIP and some calls to be placed over the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN). In contrast, this feature allows Cisco access servers to connect directly to user-side CPE devices such as PBXs and allows voice calls and data calls to be placed without requiring two different devices to be connected to the PBXs.
This feature enables the access server to provide a standard ISDN PRI network side interface to the PBXs and to mimic the behavior of legacy phone switches. To a PBX, the access server functions as a Net5 PRI switch. No change in PBX capability or behavior is required.
Benefits
The ISDN Network Side for ETSI Net5 PRI feature provides the following benefits:
•Allows you to bypass PSTN tariffed services such as trunking and administration, thus extending the cost savings of VoIP.
•Allows your PBXs to be connected directly to a Cisco access server, so PBX station calls can be routed automatically to the IP network without the need for special IP telephones.
•Provides flexibility in network design.
Related Documents
The following online document, Voice over IP for the Cisco AS5800, describes VoIP capabilities and the broader configuration context on the Cisco AS5800 network access server:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/access/nubuvoip/voip5800/
Platform Support
| Cisco IOS Support 1 | 1751, 17603 | 2600 | 2600XM/2650XM | 36204, 3640 2 | 3660 2 | 2691, 3725, 3745 | VG200 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VIC-2BRI-S/T-TE 2-Port ISDN BRI VIC, S/T interface, TE | Not Supported | 12.0(2)XD, 12.0(3)T, 12.0XK, 12.1(1), 12.1(1)T, 12.2(1), 12.2(2)T,12.2(2)XT, 12.2(11)YT, 12.3(1) | All Cisco IOS Software Versions | 12.0(7)XK, 12.1(1)T, 12.1(5)YB, 12.1(5)YD, 12.2(1), 12.2(2)T, 12.2(2)XT, 12.2(11)YT, 12.2(15)ZJ, 12.3(1), 12.3(2)T | All Versions | All Cisco IOS Software Versions | |
| VIC-2BRI-NT-TE 2-Port ISDN BRI VIC, S/T interface, NT, TE | All Versions | 12.1(3)XI, 12.1(5)T,12.1(5)YB, 12.1(5)YD, 12.2(1), 12.2(2)T, 12.2(2)XT, 12.2(11)YT, 12.3(1) | 12.2(8)T1,12.2(11)T, 12.2(11)YT, 12.2(12), 12.2(15)ZJ, 12.3(1), 12.3(2)T | 12.1(3)XI, 12.1(5)T, 12.1(5)YB, 12.1(5)YD, 12.2(1), 12.2(2)T, 12.2(2)XT, 12.2(11)YT, 12.2(15)ZJ, 12.3(1) | 12.1(3)XI, 12.1(5)T, 12.1(5)YB, 12.1(5)YD, 12.2(1), 12.2(2)T, 12.2(2)XT, 12.2(11)YT, 12.2(15)ZJ, 12.3(1) | 12.2(11)YT, 12.2(13)T, 12.2(15)ZJ, 12.3(1), 12.3(2)T, 12.3(4)XD | 12.1(5)T, 12.2(1), 12.2(2)T, 12.3(1) |
| VIC2-2BRI-NT-TE 2-Port ISDN BRI VIC, S/T interface, NT, TE | 12.2(15)ZL, 12.3(2)XA, 12.3(2)XC, 12.3(2)XE, 12.3(4)T, 12.3(5) | Not Supported | 12.2(15)ZJ, 12.3(4)T | 12.2(15)ZJ, 12.3(4)T (Not supported for Cisco 3620.4) | 12.2(15)ZJ, 12.3(4)T | 12.2(15)ZJ, 12.3(4)T, 12.3(4)XD | Not Supported |
1 Voice requires a Cisco IOS Software Voice feature set on the 1700 series router, and a Cisco IOS Software Plus feature set on the 2600/3600 series router.
2 Voice is not supported on the 3631 router.
3Cisco 1750 router platforms do not support the BRI VICs.
4Cisco 3620 series routers do not support the VIC2-2BRI-NT-TE cards.
Glossary
E1—Wide-area digital transmission scheme used in Europe. The clock rate of the E1 line (2.048 MHz) allows for 32 64-kbps channels, which include one channel for framing and one channel for D-channel signalling information.
ISDN—Integrated Services Digital Network. ISDN is a communications protocol, offered by telephone companies, that permits telephone networks to carry data, voice, and other traffic.
PBX—private branch exchange. Privately owned central switching office.
PRI—Primary Rate Interface. Primary rate access consists of a single 64-kbps D channel plus 23 T1 or 30 E1 B channels for voice or data.
POTS—plain old telephone service. Basic telephone service supplying standard single line telephones, telephone lines, and access to the Public Switched Telephone Network.
PSTN—Public Switched Telephone Network. PSTN refers to the local telephone company.
T1—Digital WAN carrier facility used in North America. T1 sends DS1 formatted data at 1.544 Mbps through the telephone-switching network, using AMI or B8ZS coding.
VoIP—Voice over IP.
Интерфейс базового уровня
Интерфейс базового уровня (англ. Basic Rate Interface, BRI) — предоставляет для связи аппаратуры абонента и ISDN-станции два B-канала и один D-канал. Интерфейс базового уровня описывается формулой . В стандартном режиме работы BRI могут быть одновременно использованы оба B-канала (например, один для передачи данных, другой для передачи голоса) или один из них. При одновременной работе каналов они могут обеспечивать соединение с разными абонентами. Максимальная скорость передачи данных для BRI интерфейса составляет 128кб/с. D-канал используется только для передачи управляющей информации. В режиме AO/DI (Always On/Dynamic ISDN) полоса 9,6 кбит/c D-канала используется в качестве постоянно включённого выделенного канала X.25, как правило, подключаемого к Интернет. При необходимости используемая для доступа к Интернет полоса расширяется путём включения одного или двух B-каналов. Этот режим, хотя и стандартизирован (под наименованием X.31), не нашёл широкого распространения. Для входящих соединений BRI поддерживается до 7 адресов (номеров), которые могут назначаться различными ISDN-устройствами, разделяющими одну абонентскую линию. Дополнительно обеспечивается режим совместимости с обычными, аналоговыми абонентскими устройствами — абонентское оборудование ISDN, как правило, допускает подключение таких устройств и позволяет им работать прозрачным образом. Интересным побочным эффектом такого «псевдоаналогового» режима работы стала возможность реализации симметричного модемного протокола X2 (англ.) фирмы US Robotics, позволявшего передачу данных поверх линии ISDN в обе стороны на скорости 56 кбит/c.
Наиболее распространённый тип сигнализации — Digital Subscriber System No. 1 (DSS-1), также известный как Euro-ISDN.
Используется два магистральных режима портов BRI относительно станции или телефонов — S/ТЕ и NT. Режим S/ТЕ — порт эмулирует работу ISDN телефона, режим NT — эмулирует работу станции. Отдельное дополнение — использование ISDN-телефона с дополнительным питанием в этом режиме, так как стандартно не все порты (и карты HFC) дают питание по ISDN-шлейфу (англ. inline power).
Каждый из двух режимов может быть «точка-многоточка» (англ. point-to-multi-point, PTMP) он же MSN (англ. Multiple Subscriber Number), или «точка-точка» (англ. point-to-point, PTP). В первом режиме для поиска адресата назначения на шлейфе используются номера MSN, которые, как правило, совпадают с выделенными провайдером телефонии городскими номерами. Провайдер должен сообщить передаваемые им MSN. Иногда провайдер использует так называемые «технические номера» — промежуточные MSN. Во втором режиме BRI-порты могут объединяться в транк — условную магистраль, по которой передаваемые номера могут использоваться в многоканальном режиме.
ISDN-технология использует три основных типа интерфейса BRI: U, S и T.
- U interface (англ.)русск. — одна витая пара, проложенная от коммутатора до абонента, работающая в полном или полудуплексе. К U-интерфейсу можно подключить только 1 устройство, называемое сетевым окончанием (англ. Network Termination, NT-1 или NT-2).
- S interface (англ.)русск. (S) и T interface (англ.)русск. — два идентичных на физическом уровне интерфейса, который часто упоминается как S/T интерфейс. Используются две витые пары, передача и приём. Может быть обжата как в RJ-45, так и в RJ-11 разъем/кабель. К разъему S/T интерфейса можно подключить одним кабелем (шлейфом) по принципу шины до 8 ISDN устройств — телефонов, модемов, факсов, называемых TE1 (Terminal Equipment 1). Каждое устройство слушает запросы в шине и отвечает на привязанный к нему MSN. Принцип работы во многом похож на SCSI.
- NT-1, NT-2 — Network Termination, сетевое окончание. Преобразовывает одну пару U в один (NT-1) или два (NT-2) 2-х парных S/T интерфейса (с раздельными парами для приёма и передачи). По сути, S и T — это одинаковые с виду интерфейсы, разница в том, что по S-интерфейсу можно подать питание для TE-устройств, например, телефонов, а по T — нет. Большинство NT-1 и NT-2 преобразователей умеют и то, и другое, поэтому интерфейсы чаще всего называют S/T.
ISDN BRI S/T Leased-Line WAN Interface Card
This section describes how to connect ISDN BRI S/T leased-line WICs to a network and contains the following sections:
•
•
•
•
ISDN BRI S/T Leased-Line WICs Overview
The 1-port ISDN BRI S/T leased-line WIC (WIC-1B-S/T-LL) provides a single B channel operating in leased-line mode at 64-kbps. (See .)
Figure 54 WIC-1B-S/T-LL Front Panel
ISDN BRI S/T Leased-Line WIC LEDs
The ISDN BRI S/T leased-line WIC LEDs are shown in . The functions of the LEDs are described in .
Table 11 ISDN BRI S/T Leased-Line WIC LEDs
LED
Description
B1
ISDN connection on B1 channel when blinking.
B2
ISDN connection on B2 channel (not used).
OK
ISDN port has established a connection with the central office switch (D channel).
|
Always off for 64 kbps, which is available on B1 only. |
Prerequisites for Connecting an ISDN BRI S/T Leased-Line WIC to a Network
Before connecting a WIC to the network, ensure that the WIC is installed in the router, the equipment is properly grounded, and you have the proper cables for connecting the WIC to the network. This section describes the preparation necessary before connecting an ISDN BRI U WIC to the network.
Grounding
Ensure that the equipment you are working with is properly grounded. For instructions on grounding your WIC, see Installing Cisco Interface Cards in Cisco Access Routers.
Cables
Use a straight-through RJ-48C-to-RJ-48C BRI cable (not included) to connect an ISDN BRI S/T leased-line WIC to a network.
Connecting an ISDN BRI S/T Leased-Line WIC to a Network
Warning Hazardous network voltages are present in WAN ports regardless of whether power to the unit is OFF or ON. To avoid electric shock, use caution when working near WAN ports. When detaching cables, detach the end away from the unit first. Statement 1026
Warning The ISDN connection is regarded as a source of voltage that should be inaccessible to user contact. Do not attempt to tamper with or open any public telephone operator (PTO)-provided equipment or connection hardware. Any hardwired connection (other than by a nonremovable, connect-one-time-only plug) must be made only by PTO staff or suitably trained engineers. Statement 23
To connect an ISDN BRI S/T leased-line WIC to a network, follow these steps:
Step 1 Confirm that the router is turned off.
Step 2 Connect one end of the straight-through RJ-48C cable to the RJ-48C port on the ISDN BRI S/T leased-line WIC.
Step 3 Connect the other end of the cable to the NT1 device, as shown in .
Figure 55 Connecting the ISDN BRI S/T Leased Line Card to an NT1 Device
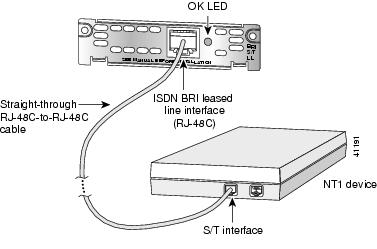
Step 4 Connect the NT1 device to the ISDN wall jack according to the documentation that came with the NT1 device.
Step 5 Turn on power to the router.
Step 6 Check that the OK LED goes on, which indicates that the ISDN port has established a connection with the central office switch.
Типы
Существует в основном 2 типа широко используемых линий ISDN. Как правило, они различаются по количеству и типам каналов, которые проходят через каждую линию. Кроме того, поскольку количество доступных каналов в линии влияет на ее возможности передачи данных, эти линии также различаются по функциональности.
Линия ISDN с базовой скоростью передачи данных (BRI)
Линия BRI, также называемая интерфейсом базовой ставки, обычно используется для подключения дома или малого бизнеса. Линия BRI имеет конфигурацию 2B+D, что означает, что она содержит 2 B канала, которые передают данные о полезной нагрузке. Каждый канал B обеспечивает полосу пропускания 64 Кбит/с. Дополнительный канал D обеспечивает подключение для передачи сигнализации и управления данными в каналах B. Сигнализация проходит по каналу D со скоростью 16 Кбит/сек.
Линия ISDN первичной скорости (PRI)
Это также называется интерфейсом первичной скорости. Линии PRI различаются в зависимости от места подключения. В Европе и Австралии конфигурация 30B + D используется для обеспечения пропускной способности 2…048 Мбит/с, в то время как в Северной Америке и некоторых частях Азии конфигурация 23B + D устанавливает соединение, обеспечивающее скорость передачи данных 1.544 Мбит/с. В Европе и Австралии используется конфигурация 30B + D, в то время как в некоторых странах Азии конфигурация 23B + D устанавливает соединение, обеспечивающее скорость передачи данных 1.544 Мбит/с. Линии PRI обеспечивают более высокую скорость передачи данных, чем BRI-соединение, и в основном используются крупными компаниями и компаниями. Соединение PRI использует 4 провода или 2 пары, при этом каждая пара предназначена для передачи данных в одном направлении.
Другим типом линии ISDN является линия Always On Dynamic ISDN (AODI). Недавно B-ISDN, или широкополосная ISDN, теперь использует волоконно-оптические кабели для создания широкополосного соединения ISDN, способного передавать данные на скоростях выше 1,5 Мбит/сек.
interface Dchannel
To specify an ISDN D-channel interface and enter interface configuration mode, use the interface Dchannel command in global configuration mode.
interface Dchannel interface-number
Syntax Description
|
interface-number |
Specifies the ISDN interface number. Note The interface-number argument depends on which controller the rlm-group subkeyword in the pri-group timeslots controller configuration command uses. For example, if the Redundant Link Manager (RLM) group is configured using the controller e1 2/3 command, the D-channel interface command will be interface Dchannel 2/3. |
pri-group timeslots
To specify an ISDN PRI group on a channelized T1 or E1 controller, and to release the ISDN PRI signaling time slot, use the pri-group timeslots command in controller configuration mode. To remove or change the ISDN PRI configuration, use the no form of this command.
pri-group timeslotstimeslot-range nfas_d {backup | none | primary {nfas_int number | nfas_group number | rlm-group number}} | service
no pri-group timeslotstimeslot-range nfas_d {backup | none | primary {nfas_int number | nfas_group number | rlm-group number}} | service
Syntax Description
|
timeslot-range |
Specifies a value or range of values for time slots on a T1 or E1 controller that comprise an ISDN PRI group. Use a hyphen to indicate a range. Note Groups of time slot ranges separated by commas (1-4,8-23 for example) are also accepted. |
|
nfas_d {backup | none | primary} |
(Optional) Configures the operation of the ISDN PRI D channel. •backup—The D-channel time slot is used as the Non-Facility Associated Signaling (NFAS) D backup. •none—The D-channel time slot is used as an additional B channel. •primary—The D-channel time slot is used as the NFAS D primary. The primary keyword requires further interface and group configuration: |
|
primary {nfas_int number| nfas_group number| rlm-group number} |
–nfas_int number—Specify the provisioned NFAS interface as a value; value is a number from 0 to 8. –nfas_group number—Specify the NFAS group. –rlm-group number—Specify the Redundant Link Manager (RLM) group and release the ISDN PRI signaling channel |
|
service |
(Optional) Configures service type mgcp for Media Gateway Control Protocol service. |
Defaults
There is no ISDN PRI group configured. The switch type is automatically set to the National ISDN switch type (primary-ni keyword)when the pri-group timeslots command is configured with the rlm-group subkeyword.
Configuration Tasks
See the following section for configuration tasks for the ISDN Network Side for ETSI Net5 PRI feature:
• (required)
Configuring ISDN Network Side for ETSI Net5 PRI
To configure the access server for ISDN Network Side for ETSI Net5 PRI, you can configure the primary-net5 switch type globally or you can configure the primary-net5 switch type on selected PRI interfaces. To configure ISDN Network Side for Net5, use the following commands beginning in global configuration mode:
|
Command |
Purpose |
|
|---|---|---|
|
Step 1 |
Router(config)# isdn switch-type primary-net5 or Router(config-if)# interface serial0/0/0:15 Router(config-if)# switch-type primary-net5 |
Sets the primary-net5 global ISDN switch type. or Specifies a D-channel interface to configure for ISDN Network Side for ETSI Net5 PRI. Sets the primary-net5 switch type on the interface. |
|
Step 2 |
Router(config-if)#isdn protocol-emulate network |
Enables network side support on the interface. |
Repeat the configuration steps on all the additional PRI D-channel interfaces you want to configure for ISDN Network Side for ETSI Net5 PRI.
Verifying ISDN Network Side for ETSI Net5 PRI
Enter the show isdn status command to learn whether ISDN Network Side for ETSI Net5 PRI is configured successfully:
router# show isdn status serial 0:15
Global ISDN Switchtype = primary-5ess
ISDN Serial0:15 interface
******* Network side configuration *******
dsl 0, interface ISDN Switchtype = primary-net5
Platform Support
| Platform | Cisco 1601(R), Cisco 1602 (R), Cisco 1605-R | Cisco 1603, Cisco 1603-R, Cisco 1604, Cisco 1604-R | Cisco 1720, 1750, 1760 | Cisco 2600, 2600XM | Cisco 3620, Cisco 3640 | Cisco 3631 | Cisco 3660 | Cisco 2691, 3725, 3745 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carrier Module | Not Required | Not Required | Not Required | on-board | NM- 2W | NM-1E2W, NM-1E1R2W, NM-2E2W | NM-1FE2W, NM-1FE1R2W, NM-2FE2W, NM-2W | Not Required | NM-1E2W, NM-1E1R2W, NM-2E2W | NM-1FE2W, NM-1FE1R2W, NM-2FE2W, NM-2W | on-board | NM-1FE2W, NM-1FE1R2W, NM-2FE2W, NM-2W |
| WIC-1B-S/T | All Cisco IOS Software releases | not supported | all Cisco IOS Software releases | all Cisco IOS Software releases | All Cisco IOS Software Releases 11.2(4)XA, 11.2(5)P, all 11.3, 11.3T, all 12.x | all Cisco IOS Software releases | All Cisco IOS Software releases | All Cisco IOS Software releases | ||||
| WIC36-1B-S/T | not supported | not supported | not supported | not supported | 11.x, 12.0, 12.0T, 12.1, 12.1T, 12.2. Not supported in 12.2T. | not supported | not supported | not supported |
Main Features
- Nearly all ISDN standards and variants are supported. Variants for T1 analyzers include AT & T #4ESS, AT & T #5ESS, Bellcore #5ESS, National ISDN 2, Nortel, DMS — 250, and Siemens EWSD, while for E1, Variants are Belgium, China, Europe, France, Britain, Germany, and Sweden
- 1 to 4 Configurable Signaling Links.
- Supported protocol layers — LAPD and Q.931 Layers
- Switch and Subscriber Emulation
- User Friendly GUI for Configuring the ISDN Layer parameters. Includes configuring for Called/Calling Numbering Plan/Type, type of ISDN service, etc.
These ISDN parameters may be saved within a Timeslot group so as to allow multiple ISDN parameter configurations, simultaneously. - Quick configuration for Called & Calling Number
- Provides various release cause codes such as rejected, no user response, user busy, congested, and so on to troubleshoot the problems in ISDN
- Simple NFAS setup for T1.
- Single/Dual T1, Single/Dual E1 Interfaces for the ISDN Signaling Links.
- Call Records for Complete or Incomplete Calls
- Companion product «ISDN Protocol Analyzer» displays all ISDN Messages in Real Time.
- Place call or accept call for each timeslot or for the whole trunk.
- Supports Overlap Digit Sending
- Exports call records to a TEXT file.
- Displays Lap D (Layer 2) statistics
Known Issues
Some of the known issues with the BRI VICs are discussed in this section.
When the BRI voice interfaces are configured, this error message is received:
This is because the VIC-2BRI-S/T-TE can have more B channels than the Voice Network Module can handle. The NM-1V can handle two voice calls (has two DSPs). The NM-2V can handle four voice calls (four DSPs). For more information on this, refer to the error message %C542-1-INSUFFICIENT_DSPS (registered customers only) in the Error Message Decoder (registered customers only)
Another known problem is due to Cisco bug ID CSCdv00152 (registered customers only) .
The compand-type a-law command does not exist on the CLI for a BRI port.
This bug restricted the use of the
BRI-VIC
Features
| WIC36-1B-S/T | WIC-1B-S/T |
|---|---|
|
|
Технические характеристики
На физическом уровне характеристики интерфейса E1 соответствуют стандарту ITU-T G.703.
Основные рабочие характеристики интерфейса:
- Номинальная битовая скорость 2048 кбит/c
- Частота тактового генератора 2048000±20 Гц (относительная стабильность частоты ±10×10−6{\displaystyle \pm 10\times 10^{-6}})
- Схема кодирования HDB3 (двуполярная высокоплотная схема)
- Отдельные линии приёма и передачи:
- По одному коаксиальному кабелю на приём и передачу (сопротивление — 75 Ом)
- По одной симметричной витой паре на приём и передачу (сопротивление — 120 Ом)
Использование классического кабеля UTP cat5e (сопротивление 85-115 Ом) не предусмотрено стандартом, однако это возможно, пока вклад рассогласования по сопротивлению меньше способности оборудования фильтровать шумы.
show isdn
To display the information about memory, Layer 2 and Layer 3 timers, and the status of PRI channels, use the show isdn command in EXEC mode.
show isdn {active dsl|serial-number] | history dsl |serial-number] | memory | servicedsl | serial-number] | status dsl | serial-number | timers dsl| serial-number]}
Syntax Description
|
active dsl|serial-number |
Displays current call information of all ISDN interfaces or, optionally, a specific digital subscriber line (DSL) or a specific ISDN PRI interface (created and configured as a serial interface). Values of dsl range from 0 to 15. Information displayed includes the called number, the remote node name, the seconds of connect time, the seconds of connect time remaining, the seconds idle, and Advice of Charge (AOC) charging time units used during the call. |
|
history dsl|serial-number |
Displays historic and current call information of all ISDN interfaces or, optionally, a specific DSL or a specific ISDN PRI interface (created and configured as a serial interface). Values of dsl range from 0 to 15. Information displayed includes the called number, the remote node name, the seconds of connect time, the seconds of connect time remaining, the seconds idle, and AOC charging time units used during the call. |
|
memory |
Displays ISDN memory pool statistics. This keyword is for use by technical development staff only. |
|
service dsl|serial-number |
Displays the service status of all ISDN interfaces or, optionally, a specific DSL or a specific ISDN PRI interface (created and configured as a serial interface). Values of dsl range from 0 to 15. |
|
status dsl|serial-number |
Displays the status of all ISDN interfaces or, optionally, a specific DSL or a specific ISDN PRI interface (created and configured as a serial interface). Values of dsl range from 0 to 15. |
|
timers dsl|serial-number |
Displays the values of Layer 2 and Layer 3 timers for all ISDN interfaces or, optionally, a specific DSL or a specific ISDN PRI interface (created and configured as a serial interface). Values of dsl range from 0 to 15. |